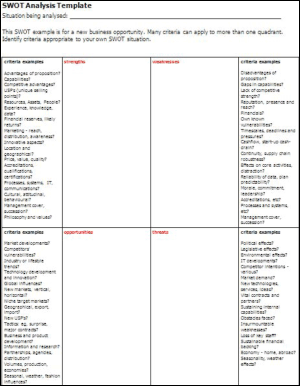
Usually displayed as a quadrant diagram summarizing a unit’s assessment of its strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats in relation to a specific problem, challenge or venture. Identifying these four factors is valuable when trying to decide whether or not to embark on a course of action/venture by weighing the pros and cons in a chart form. Best done by surveying knowledgeable stakeholders across a range of responsibilities within the group. See: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWOT_Analysis
© Alan Chapman 2005-09. Free PDF version of this tool and information about SWOT analysis methods are available at www.businessballs.com/swotanalysisfreetemplate.htm. This is a free resource from www.businessballs.com, which contains lots more useful tools, diagrams and materials. Not to be sold or published.
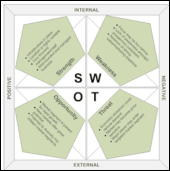
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors and opportunities and threats are external factors. A SWOT diagram analyzes a project or business venture by focusing on each of these factors. It typically consists of four boxes, one for each area, but the exact shape may vary depending on the design.
Typical Uses
SWOT diagrams can be especially useful when trying to decide whether or not to embark on a certain venture by determining if the pros outweigh the cons. By clearly outlining all positives and negatives concerning the project, it will be easier to decide whether or not it is really worth it.
Best Practices
Determine the objective.
Decide on a key objective to analyze and place it at the top of the page.
Create a grid.
Draw a large square, then divide it into four smaller squares.
Label each box.
Write the word "Strengths" inside the top left box, "Weaknesses" inside the top right box, "Opportunities" within the bottom left box, and "Threats" inside the bottom right box. These are titles, so they should be distinguished from the rest of the text to be put in the boxes using color and font. SmartDraw offers several SWOT diagram templates designed to make construction quick and easy.
Fill the diagram.
Add factors that affect the project to the box to which they apply. Factors are typically listed with bullets.
Label the grid.
On top of the top left box write the word "Positive." Both boxes beneath, "Strengths" and "Opportunities," are positive for the company. On top of the top right box write "Negative." Both boxes beneath it contain negative effects to the company. Along the side of the top right box write the word "Internal." Both "Strengths" and "Weaknesses" pertain to the abilities and resources within the company. Next to the bottom left box write the word "External." "Opportunities" and "Threats" are both generated by the outside world.
Draw conclusions.
Analyze the finished SWOT diagram. Be sure to notice if the positive outcomes outweigh the negative. If they do, it may be a good decision to carry out the objective. If they do not, adjustments may need to be made, or else the plan should simply be aborted.